

0755-23321087
Asynchronous motors (also called induction motors) fall into the same category of AC motors as synchronous motors. In terms of function they are divided into two types: motor and generator. According to the number of phases there are single-phase asynchronous motors, three-phase asynchronous motors, single-phase synchronous motors and three-phase synchronous motors. Among them three-phase synchronous motors can be divided into electric excitation synchronous motor and permanent magnet synchronous motor according to whether there is a permanent magnet (because its working principle is similar to that of DC motor and foreign countries do not distinguish the waveform of back electromotive force, hence also known as BLDC DC motor). We will use three-phase asynchronous motor and three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor as examples to describe the working principle of AC motor.
1. Three-phase AC motor
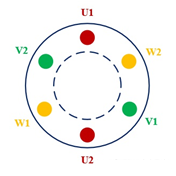
When the three-phase AC motor is running, its three-phase stator winding is connected to the three-phase AC power supply, where the three-phase AC current is provided by the power supply and a rotating magnetic field is generated inside the motor. The magnetic field is linked with stator windings and rotor windings to realizethe transfer and the transformation of energy from the stator to the rotor. The stator winding of the three-phase AC motor is a three-phase symmetrical winding and the angle of 2 adjoining axes is 120° in geometrical space. As shown in the figure below, the red, the yellow and green lines respectively represent the UVW three phases of the motor stator winding.
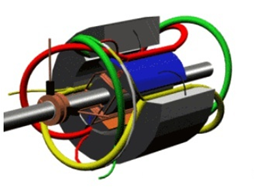
The figure below shows a schematic cross-sectional view of the motor winding.
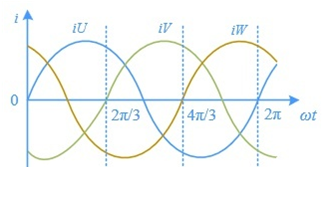
During normal operation, the current waveform of the three-phase AC motor stator is a sinusoidal wave with a phase difference of 120°, as shown in the figure below. The three-phase combined magnetic field rotates in space, the current changes for one cycle and the rotating magnetic field rotates then once in space. Therefore the rotational speed of the rotating magnetic field formed by the three-phase current in the stator winding is called the synchronous rotational speed 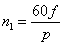 , where f is the three-phase electrical frequency, p is the number of pole pairs of the motor.
, where f is the three-phase electrical frequency, p is the number of pole pairs of the motor.
2. Three-phase asynchronous motor
The rotor structure of the three-phase asynchronous motor is similar to the stator and its cross-section can be understood as the composition of many wires connected end to end, as shown in the figure below.
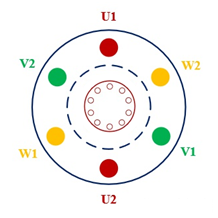
When the asynchronous motor is working, the stator winding is connected to the three-phase power supply. According to the above analysis the three-phase current passes through the three-phase winding to form a rotating magnetic field that rotates at the synchronous speed n1. The rotating magnetic field and the rotor conductor have a relative cutting motion. According to the principle of electromagnetic induction the rotor conductor (the rotor winding is a closed path) generates an induced electromotive force (the direction of the induced electromotive force is determined by the right-hand rule) and then generates an induced current that is consistent with the direction of the induced electromotive force. The current-carrying rotor conductor is subjected to electromagnetic force in the magnetic field generated by the stator. The left-hand rule can determine the force direction of each rotor conductor, and then drive the rotor to rotate in the direction of the rotating magnetic field.
Because the induced current in the rotor coil of the three-phase asynchronous motor is caused by the relative movement of the rotor conductor and the magnetic field. The rotor speed of the three-phase asynchronous motor will not be synchronized with the rotating magnetic field, nor will it exceed the speed of the rotating magnetic field. Therefore, the rotor rotation speed of the three-phase asynchronous motor cannot be the same as the rotating magnetic field and is always less than the synchronous speed of the rotating magnetic field, so there will be a speed difference (called slip). Because the rotor speed is different from the stator magnetic field speed, it is called an asynchronous motor.
3. Three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor
The rotor excitation of the three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor is a permanent magnet, which can be divided into surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor and embedded permanent magnet synchronous motor according to the embedding method of the permanent magnet. For the permanent magnet synchronous motor, it can be understood as the following figure, in which the rotor has two magnetic poles, N pole and S pole.
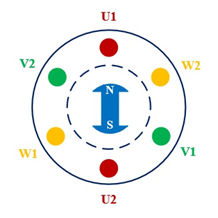
When the synchronous motor is working, the stator winding is connected to the three-phase power supply. According to the above analysis, the three-phase current passes through the three-phase winding to form a rotating magnetic field that rotates at a synchronous speed n1. Under the principle of “repulsion of same magnetic poles and attraction of opposite” the rotationg magnetic field will pull the rotor to rotate at the same speed. As the rotor rotates at the same speed, the rotor speed n of the synchronous motor is the same as the synchronous speed n1.
4. Summary
(1) For permanent magnet synchronous motors and asynchronous motors, the stator windings are all connected to three-phase AC voltage to generate a rotating magnetic field with the same frequency as the voltage and current.
(2) The permanent magnet synchronous motor does not need electric excitation and has high efficiency; the rotor winding of the asynchronous motor requires additional energy for excitation and this part of the current is consumed in the form of heat dissipation in the rotor, which reduces the efficiency of the motor.
(3) The control of permanent magnet synchronous motor is more likely to fall out of step., whereas the control of asynchronous motor is simple and VVVF control can be used. But high-precision speed sensorless vector control is more difficult and the requirements for the drive are relatively higher.